LENGTH( )
The LENGTH( ) function returns the number of bytes in its string argument
after deleting all trailing spaces.
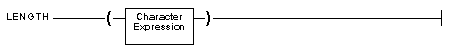 The LENGTH( ) function returns an integer value, based on the length (in
bytes) of its character-expression argument.
The following are among the possible uses for the LENGTH( ) function:
You can check whether a user has entered a database name and, if not, set a
default name.
Check whether the user has supplied the name of a file to receive the output
from a report and, if not, set a default output.
Check whether a file name is longer than n characters (and therefore not DOS
compatible).
Use LENGTH(string) as the maximum value in a FOR loop, and then check each
character in string for a specific character. For example, you can check for . to
determine whether a table name has an owner prefix.
Using LENGTH( ) in SQL Expressions
Unlike some other built-in functions of 4GL, you can use LENGTH( ) in SQL
statements, as well as in other 4GL statements. LENGTH( ) can also be called from a
C function. (That is, the database engine supports a function of the same name
and of similar functionality.)
In a SELECT or UPDATE statement, the argument of LENGTH( ) is the identifier
of a character column. In this instance, LENGTH( ) returns the number of bytes
in the CLIPPED data value (for CHAR or VARCHAR columns) or the full number of
bytes (for TEXT and BYTE data types).
The LENGTH( ) function can also take the name of a database column as its
argument, but only within an SQL statement.
References
CLIPPED
USING
The LENGTH( ) function returns an integer value, based on the length (in
bytes) of its character-expression argument.
The following are among the possible uses for the LENGTH( ) function:
You can check whether a user has entered a database name and, if not, set a
default name.
Check whether the user has supplied the name of a file to receive the output
from a report and, if not, set a default output.
Check whether a file name is longer than n characters (and therefore not DOS
compatible).
Use LENGTH(string) as the maximum value in a FOR loop, and then check each
character in string for a specific character. For example, you can check for . to
determine whether a table name has an owner prefix.
Using LENGTH( ) in SQL Expressions
Unlike some other built-in functions of 4GL, you can use LENGTH( ) in SQL
statements, as well as in other 4GL statements. LENGTH( ) can also be called from a
C function. (That is, the database engine supports a function of the same name
and of similar functionality.)
In a SELECT or UPDATE statement, the argument of LENGTH( ) is the identifier
of a character column. In this instance, LENGTH( ) returns the number of bytes
in the CLIPPED data value (for CHAR or VARCHAR columns) or the full number of
bytes (for TEXT and BYTE data types).
The LENGTH( ) function can also take the name of a database column as its
argument, but only within an SQL statement.
References
CLIPPED
USING
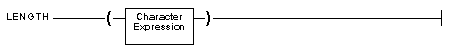 The LENGTH( ) function returns an integer value, based on the length (in
bytes) of its character-expression argument.
The following are among the possible uses for the LENGTH( ) function:
You can check whether a user has entered a database name and, if not, set a
default name.
Check whether the user has supplied the name of a file to receive the output
from a report and, if not, set a default output.
Check whether a file name is longer than n characters (and therefore not DOS
compatible).
Use LENGTH(string) as the maximum value in a FOR loop, and then check each
character in string for a specific character. For example, you can check for . to
determine whether a table name has an owner prefix.
Using LENGTH( ) in SQL Expressions
Unlike some other built-in functions of 4GL, you can use LENGTH( ) in SQL
statements, as well as in other 4GL statements. LENGTH( ) can also be called from a
C function. (That is, the database engine supports a function of the same name
and of similar functionality.)
In a SELECT or UPDATE statement, the argument of LENGTH( ) is the identifier
of a character column. In this instance, LENGTH( ) returns the number of bytes
in the CLIPPED data value (for CHAR or VARCHAR columns) or the full number of
bytes (for TEXT and BYTE data types).
The LENGTH( ) function can also take the name of a database column as its
argument, but only within an SQL statement.
References
CLIPPED
USING
The LENGTH( ) function returns an integer value, based on the length (in
bytes) of its character-expression argument.
The following are among the possible uses for the LENGTH( ) function:
You can check whether a user has entered a database name and, if not, set a
default name.
Check whether the user has supplied the name of a file to receive the output
from a report and, if not, set a default output.
Check whether a file name is longer than n characters (and therefore not DOS
compatible).
Use LENGTH(string) as the maximum value in a FOR loop, and then check each
character in string for a specific character. For example, you can check for . to
determine whether a table name has an owner prefix.
Using LENGTH( ) in SQL Expressions
Unlike some other built-in functions of 4GL, you can use LENGTH( ) in SQL
statements, as well as in other 4GL statements. LENGTH( ) can also be called from a
C function. (That is, the database engine supports a function of the same name
and of similar functionality.)
In a SELECT or UPDATE statement, the argument of LENGTH( ) is the identifier
of a character column. In this instance, LENGTH( ) returns the number of bytes
in the CLIPPED data value (for CHAR or VARCHAR columns) or the full number of
bytes (for TEXT and BYTE data types).
The LENGTH( ) function can also take the name of a database column as its
argument, but only within an SQL statement.
References
CLIPPED
USING